In Depth
Supersaurus is a relative of the ever famous Diplodocus and Apatosaurus (formerly known as Brontosaurus), as these three genera are all described as diplodocid sauropods. Diplodocids are members of the Diplodocidae and are noted for their long necks and tails, the latter of which are very thin and whip-like. Diplodocids can be further divided into two groups, diplodocines which are closer to Diplodocus and are fairly gracile (lightly built), and apatosaurines that are closer to Apatosaurus and more robust (heavily built). Of these, Supersaurus has usually been perceived to be closer to Apatosaurus, though one study (Whitlock, 2011) has proposed that Supersaurus is more advanced in form than Apatosaurus, and should therefore be classed as a diplodocine and closer to Diplodocus.
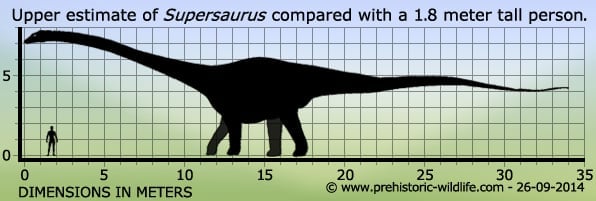
Supersaurus was exceptionally large, even for the type of dinosaur that the genus represents. So far all Supersaurus fossils have been recovered from the world famous Morrison Formation of North America, which is a clear indicator that Supersaurus lived during the late Jurassic, which was the high point for sauropod diversity in North America. Other diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs that Supersaurus may have encountered include Kaatedocus, Eobrontosaurus, Suuwassea and Amphicoelias, while other sauropod types such as Camarasaurus and Brachiosaurus were also roaming around.
It is now known that the genera Dystylosaurus and Ultrasauros (not to be confused with Ultrasaurus) are actually synonymous with Supersaurus. Both of these genera were based upon the description of vertebrae that were later identified as belonging to Supersaurus. In fact the vertebra used to base the description of Ultrasauros is actually thought to have come from the same individual Supersaurus that became the genus holotype.
Further Reading
- Three new sauropod dinosaurs from the Upper Jurassic of Colorado. Great Basin Naturalist, 45: 697-709. - J. A. Jenson - 1985. - A re-assessment of Ultrasauros macintoshi (Jensen, 1985). - Pp. 87-95 in M. Morales (ed.), The Continental Jurassic: Transactions of the Continental Jurassic Symposium, Museum of Northern Arizona Bulletin number 60. - B. Curtice, K. Stadtman & L. Curtice - 1996. - The demise of Dystylosaurus edwini and a revision of Supersaurus vivianae. B. Curtice & L. Stadtman. - In R. D. McCord & D. Boaz (eds.). Western Association of Vertebrate Paleontologists and Southwest Paleontological Symposium, Proceedings 2001. Mesa Southwest Museum Bulletin 8. pp. 33–40. - Morphology of a specimen of Supersaurus (Dinosauria, Sauropoda) from the Morrison Formation of Wyoming, and a re-evaluation of diplodocid phylogeny. - Arquivos do Museu Nacional 65 (4): 527–544. - David M. Lovelace, Scott A. Hartman & William R. Wahl - 2007. - A phylogenetic analysis of Diplodocoidea (Saurischia: Sauropoda).” Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. - J. A. Whitlock - 2011.