In Depth
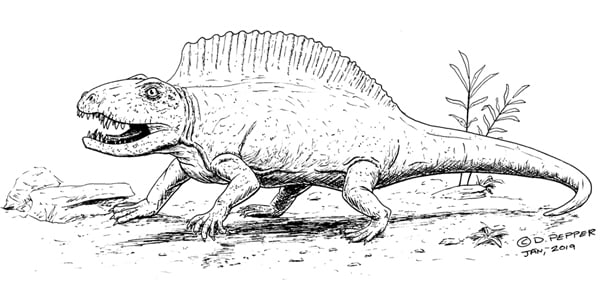
Ctenospondylus was one of the larger sail-backed synapsids. So far only known from the central united states it is probable though thatCtenospondylus had a wider distribution, at least in North America, though the lack of known fossil bearing rock formations from the Permian is limited to just a few areas.
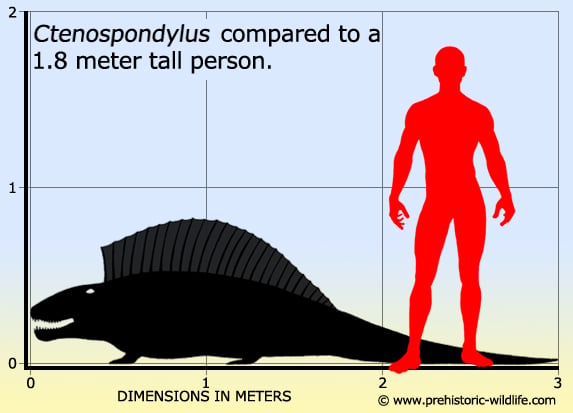
Ctenospondylus is classed as a sphenacodontid, a member of the Sphenacodontidae which is a group typified by the type genus Sphenacodon, though this genus seems to lack a sail. At up to three meters long, Ctenospondylus would have been amongst the larger predators of their ecosystem, and may have hunted other smaller synapsids, especially herbivorous ones such as caseiids like Casea. However even Ctenospondylus was dwarfed by some pelycosaur herbivores, such as the caseiid Cotylorhynchus.
Like with other sail-backed pelycosaurs, the sail on the back of Ctenospondylus is believed to have been primarily for thermoregulation of body temperature, though it may have additionally served a display purpose so that individuals of Ctenospondylus could identify one another from other kinds of sail-backed synapsids. Examples of these include the famous Dimetrodon, Secodontosaurus, and Edaphosaurus, which are also known to have been around and active in the same locations at the same times as Ctenospondylus.
At the time of writing the type species of Ctenospondylus, C. casei, is known from Texas and Utah, while the second species C. ninevehensis is known from Ohio.
Further Reading
- Studies on American Permo-Carboniferous reptiles. - Problems of Paleontology 1:85-93 - A. S. Romer - 1936. - Global Permian tetrapod biostratigraphy and biochronology In S. G. Lucas, G. Cassinis & J. W. Schneider - Non-Marine Permian Biostratigraphy and Biochronology. Special Publications 265. London: Geological Society. pp. 65–93 - S. G. Lucas - 2006.