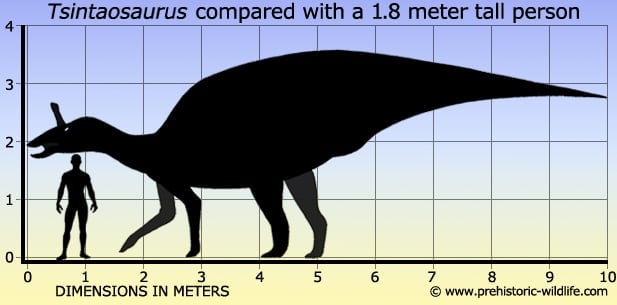
In Depth
One of the more popular hadrosaurids, Tsintaosaurus is actually not known by many individuals. The popularity of Tsintaosaurus is all down to the forward pointing crest that adorns the top of the skull. There was one widespread speculation that this crest was simply a product of the fossilisation process, and that the bone that made up the crest was actually from somewhere else, something that further led to speculation that Tsintaosaurus was actually the same genus of dinosaur as the hadrosauroid Tanius. A further specimen was eventually found however, and again the forward pointing crest was evident and in exactly the same place as the first. This revealed that the crest is indeed that same as it was in the living animals and that while both Tsintaosaurus and Tanius are related, they are very different genera. In 2013 a study (Prieto-M�rquez & Wagner) resulted in a new reconstruction for the head crest for Tsintaosaurus. Instead of a simples spike, the crest actually rose up from the nasal bones and curved around above the back of the skull.
Like with other hadrosaurs, would have probably been primarily quadrupedal, though bipedal stances and locomotion were also easily possibly. This flexibility meant that Tsintaosaurus were also capable of feeding at varying heights, increasing the amount of suitable plants for feeding. Because the crest of Tsintaosaurus is hollow it is classed as a lambeosaurine hadrosaurid, the group that contains all hadrosaurids that have hollow crests (after the type genus of the group Lambeosaurus, the first hollow crested hadrosaurid identified). As a reasonably large animal, and a plant eater, Tsintaosaurus was likely prey for large predatory dinosaurs of the time such as tyrannosaurs like Zhuchengtyrannus.
Further Reading
– The dinosaurian remains of Laiyang, Shantung. – Palaeontologia Sinica, New Series C. Whole Number. 42 (16): 1–138. – C. -C. Young – 1958. – Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus Young and Tanius sinensis Wiman: a preliminary comparative study of two hadrosaurs (Dinosauria) from the Upper Cretaceous of China. – 2. 317. C.R. Academy of Science Paris: 1255–1261. – E. Buffetaut & H. Tong – 1993. – Pararhabdodon isonensis and Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus: a new clade of lambeosaurine hadrosaurids from Eurasia. – Cretaceous Research. – A. Prieto-M�rquez & J. R. Wagner – 2009. – The ‘Unicorn’ Dinosaur That Wasn’t: A New Reconstruction of the Crest of Tsintaosaurus and the Early Evolution of the Lambeosaurine Crest and Rostrum. – PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e82268. – A. Prieto-M�rquez & J. R. Wagner – 2013. .