Dimetrodon: Fossils Map
Discover 94+ Fossil Records of Dimetrodon with our interactive fossil map and geographical timeline chart.
The fossil map pinpoints discovery sites worldwide, click each marker to see fossil ages and detailed references..
The interactive bar chart reveals how many Dimetrodon fossils were found across different geological ages, helping you visualize its prehistoric history and global distribution.
In Depth about Dimetrodon
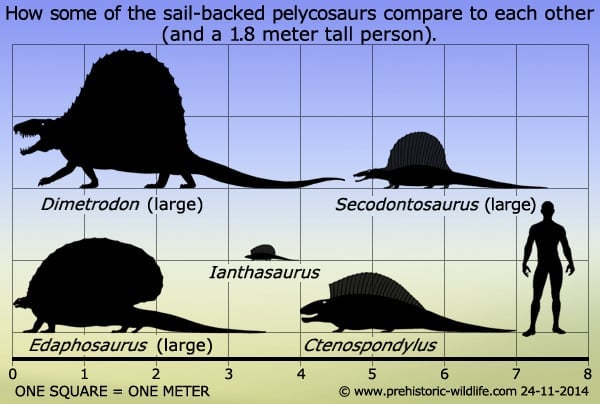
Often considered a dinosaur, Dimetrodon was actually one of the pelycosaurs and predated the earliest dinosaurs by tens of millions of years.
Dimetrodon is NOT a dinosaur, it lived about 40 million years before dinosaurs appeared and is a distant relative of mammals.
With its sharp teeth and powerful jaws, it was one of the top land predators long before dinosaurs appeared.
Its popularity comes from the massive sail that is carried erect on its back, the exact purpose of which is still unknown, but it has been speculated to being for display purposes either to attract mates or intimidate rivals.
Another theory is that it was used for temperature regulation. cold blooded animals are always sluggish until they can raise their body temperatures.
If Dimetrodon flushed blood into its sail to raise its temperature, it would have had a significant advantage over its prey items that would have still been too slow and sluggish to escape. It is of course entirely plausible that both theories are correct.
Dimetrodon had a very successful predator design and its broad expanse in the timeline of the fossil record and geographical distribution of remains are proof of this. Aside from the potential advantage of controlled thermoregulation, Dimetrodon had two different kinds of teeth, hence the reason for its name.
These teeth consisted of teeth designed for grabbing its prey, and teeth designed for shearing flesh. The teeth also featured very fine serration that were initially thought to be cracks.
Aside from more efficient kills, these teeth would have enabled Dimetrodon to make short work eating its prey items. Earlier examples of Dimetrodon appear smaller than the later fossils.
FAQ’s
Is a dimetrodon an amphibian
No, Dimetrodon was not an amphibian. It was a synapsid, an early type of land-dwelling vertebrate that lived during the Permian Period, about 295–272 million years ago. Synapsids are more closely related to mammals (including humans) than to amphibians or reptiles.
Are dimetrodons related to dinosaurs
No, Dimetrodons are not related to dinosaurs. They lived about 40 million years before the first dinosaurs appeared. Dimetrodon was a synapsid, an early relative of mammals, while dinosaurs belonged to the reptile group called archosaurs.
What Does Dimetrodon Eat?
Dimetrodon was a carnivore. It ate other animals, including amphibians, reptiles, and smaller synapsids that lived during the Permian Period.
Further Reading
– Descriptions of extinct Batrachia and Reptilia from the Permian formations of Texas. – Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 17:505-530. – Edward Drinker Cope – 1878.
– The history of the Pelycosauria, with a description of the genus Dimetrodon, Cope. – Transactions of the American Philosophical Society 20 (1): 5–62. – G. Baur & E. C. Case – 1899.
– Notes on the Permo-Carboniferous reptile Dimetrodon. – The Journal of Geology 35 (8): 673–689. – A. S. Romer – 1927.
– The skeleton of an immature pelycosaur, Dimetrodon cf. grandis, from the Permian of Texas. – Journal of Paleontology 16 (4): 485–486. – C. W. Sternberg – 1942.
– The San Angelo Formation, Permian of Texas, and its vertebrates. – The Journal of Geology 61 (5): 389–423. – E. C. Olsen & J. R. Beerbower – 1953.
– Parallelism in the evolution of the Permian reptilian faunas of the Old and New Worlds. – Fieldiana 37 (13): 385–401. – Everett C. Olson – 1955.
– Comparison of the Early Permian vertebrate faunas of the Four Corners region and north-central Texas. – Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History Contributions in Science 105: 1–13. – P. P. Vaughn – 1966.
– Early Permian vertebrates from southern New Mexico and their paleozoogeographic significance. – Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History Contributions in Science 166: 1–22.. – P. P. Vaughn – 1969.
– A new species of Dimetrodon (Reptilia, Pelycosauria) from a non-deltaic facies in the Lower Permian of north-central New Mexico. – Journal of Paleontology 51 (1): 108–115. – D. S. Berman – 1977.
– A thermal model of the sailback pelycosaur. – Paleobiology 12 (4): 450–458. – S. C. Haack – 1986.
– A new species of Dimetrodon (Synapsida: Sphenacodontidae) from the Lower Permian of Germany records first occurrence of genus outside of North America. – Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 38: 803–812. – D. S. Berman, R. R. Reisz, T. Martens & A. C. Henrici – 2001.
– Natural environment and thermal behaviour of Dimetrodon limbatus. – Journal of Thermal Biology 26 (1): 15–20. – G. A. Florides, S. A. Kalogirou, S. A. Tassou & L. Wrobel – 2001.
– Histological analysis of traumatic injury to multiple neural spines of an associated skeleton of Dimetrodon: Implications for healing response, dorsal sail morphology and age-at-death in a Lower Permian synapsid. – Integrated Comparative Biology 44: 628. – E. A. Rega, K. Noriega, S. Sumida & A. Lee – 2004.
– Evidence-based paleopathology I: Ontogenetic and functional implications of dorsal sails in Dimetrodon. – Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 25 (S3): 103A. – E. Rega, S. Sumida, K. Noriega, C. Pell & A. Lee – 2005.
– Evidence-based paleopathology II: Impact on phylogenetic analysis of the genus Dimetrodon. – Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 25 (S3): 120A. – S. Sumida, E. Rega & K. Noriega – 2005.
– A new record of the Early Permian pelycosaurian-grade synapsid Dimetrodon (Eupelycosauria: Sphenacodontidae) from the Lower Cutler Group (Early Permian) of Jemez Pueblo, north-central New Mexico. – Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 27 (3, Suppl.): 110A. – K. Madalena, S. Sumida, K. Zeigler & E. Rega – 2007.
– Evolution of bone microanatomy of the tetrapod tibia and its use in palaeobiological inference. – Journal of Evolutionary Biology 21 (3): 807–826. – A. Kriloff, D. Germain, A. Cranoville, P. Vincent, M. Sache & M. Laurin – 2008.
– Dimetrodon (Amniota: Synapsida: Sphenacodontidae) from the Lower Permian Abo Formation, Socorro County, New Mexico. – New Mexico Geological Society Guidebook 60. New Mexico Geological Society. pp. 281–284. – S. G. Lucas, J. A. Spielmann, L. F. Rinehart & T. Martens – 2009.
– Comparative anatomy and osteohistology of hyperelongate neural spines in the sphenacodontids Sphenacodon and Dimetrodon (Amniota: Synapsida). – Journal of Morphology 271 (12): 1407–1421. – A. K. Huttenlocker, E. Rega & S. S. Sumida – 2010.
– Healed Fractures in the Neural Spines of an Associated Skeleton of Dimetrodon: Implications for Dorsal Sail Morphology and Function. – Fieldiana Life and Earth Sciences 5: 104. – E. A. Rega, K. Noriega, S. S. Sumida, A. Huttenlocker, A. Lee & B. Kennedy – 2012.