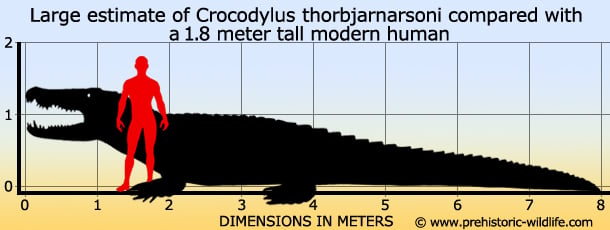
In Depth
Further Reading
A giant crocodile from the Plio-Pleistocene of Kenya, the phylogenetic relationships of Neogene African crocodylines, and the antiquity of Crocodylus in Africa. – Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 32 (3): 587. – C. A. Brochu & G. W. Storrs – 2012.